1410, PARKSON, 44-60 ZHONGSHAN ROAD, QINGDAO, CHINA
How to Safety Use Wire Rope
Wire rope is a complex mechanical device that has many moving parts all working in tandem to help support and move an object or load. In the lifting and rigging industries, wire rope is attached to a crane or hoist and fitted with swivels, shackles or hooks to attach to a load and move it in a controlled matter. It can also be used to lift and lower elevators, or as a means of support for suspension bridges or towers.
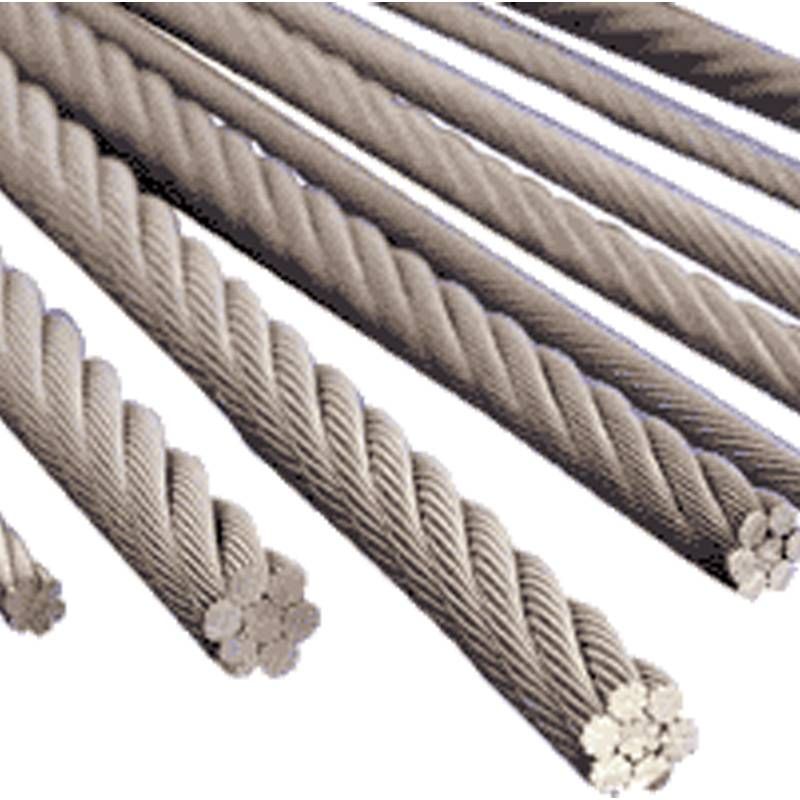

Wire rope is a preferred lifting device for many reasons. Its unique design consists of multiple steel wires that form individual strands laid in a helical pattern around a core. This structure provides strength, flexibility, and the ability to handle bending stresses. Different configurations of the material, wire, and strand structure will provide different benefits for the specific lifting application, including:
Strength
Flexibility
Abrasion resistance
Crushing resistance
Fatigue resistance
Corrosion resistance
Rotation resistance
However, selecting the proper wire rope for your lifting application requires some careful thought. Our goal is to help you understand the components of a wire rope, the construction of wire rope, and the different types of wire rope and what they might be used for. This will allow you to select the best performing and longest-lasting wire rope for the job at hand.
Components of Wire Rope
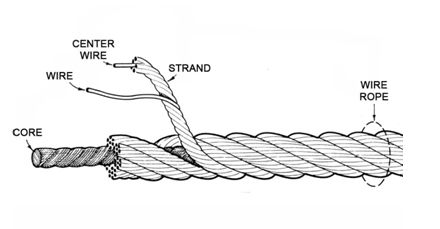
There are four basic components that make up the design of a finished wire rope:
1. Wires made from metal that form a singular strand
2. Multi-wire strands laid around a core in a helical pattern
3. A fiber or steel core
4. Lubrication
5.
Type of Wire Rope
Stainless Steel Wire Rope

Stainless steel is the standard alloy utilized in rope and cable. Its resistance to corrosion is much higher than galvanized and coated ropes, although there is no difference in strength. Therefore, it is the preferred material used in marine and salt-water based industries. It does not react easily to chemicals from food processing, textile, and photographic settings. Its high resistance to corrosion, heat and cold, pulp and paper chemicals make stainless steel wire rope a very essential material for creating precise instruments, automobiles, fishing vessels, petrochemical equipment, and other fields.
Galvanized Wire Rope

Galvanized wire rope is also a steel wire material that has undergone a galvanizing process to enhance its corrosion-resistance. The finished wire product is submerged into a zinc bath to coat its entirety, that is, galvanize it. Zinc is utilized in the process because the cathode preservation increases the life expectancy of the wire. Though the coating will wear off as time goes by, it is still resistant to rust, corrosion, and other harsh chemicals. Galvanized wire can be found in industrial and construction fields as well as agricultural and DIY projects.
Coated Wire Rope

Stainless steel and galvanized wire can be coated with PVC (poly-vinyl-chloride) or vinyl. Coated wire rope comes in various colours such as clear, black, white, or any other colour that is required in different industries. PVC coated wire is flexible, weather-resistant, and very cost-effective. Nylon coated wire, though not as flexible as PVC, is abrasion-resistant and is ideal for businesses in extremely cold regions. Wire rope can be assembled to suit specific applications.
How to Safety Use Wire Rope
1. Wire rope WILL FAIL IF WORN OUT, OVERLOADED, MISUSED, DAMAGED, or IMPROPERLY MAINTAINED.
2. In service, wire rope loses strength and work capability. Abuse and misuse increase the rate of loss.
3. The MINIMUM BREAKING STRENGTH of wire rope applies ONLY to a NEW, UNUSED rope.
4. The Minimum Breaking Strength should be considered the straight line pull with both rope ends fixed to prevent rotation, which will ACTUALLY BREAK a new, UNUSED, rope. The Minimum Breaking Strength of a rope should NEVER BE USED AS ITS WORKING LOAD.
5. To determine the working load of a wire rope, the MINIMUM or NOMINAL Breaking Strength MUST BE REDUCED by a DESIGN FACTOR (formerly called a Safety Factor). The Design Factor will vary depending upon the type of machine and installation, and the work performed. YOU must determine the applicable Design Factor for your use.
6. WIRE ROPE WEAR OUT. The strength of a wire rope slightly increases after the break in period, but will decrease over time. When approaching the finite fatigue life span the breaking strength will sharply decrease. Never evaluate the remaining fatigue life of a wire rope by testing a portion of a rope to destruction only. An indepth rope inspection must be part of such evaluations.
7. NEVER overload a wire rope. This means NEVER use the rope where the load applied is greater than the working load determined by dividing the Minimum Breaking Strength of the rope by the appropriate Design Factor.
8. NEVER ‘SHOCK LOAD’ a wire rope. A sudden application of force or load can cause both visible external damage (e.g. birdcaging) and internal damage. There is no practical way to estimate the force applied by shock loading a rope. The sudden release of a load can also damage a wire rope.
9. Lubricant is applied to the wires and strands of a wire rope when manufactured. This lubricant is depleted when the rope is in service and should be replaced periodically.
10. When a wire rope has been removed from service because it is no longer suitable, IT MUST NOT BE RE-USED ON ANOTHER APPLICATION.
11. Every wire rope user should be aware of the fact that each type of fitting attached to a wire rope has a specific efficiency rating which can reduce the working load of a rope assembly or rope system, and this must be given due consideration in determining the capacity of a wire rope system.
12. Some conditions that can lead to problems in a wire rope system include:
o Sheaves that are too small, worn or corrugated can cause damage to wire rope.
o Broken wires mean a loss of strength.
o Kinks permanently damage a wire rope.
o Environmental factors such as corrosive conditions and heat can damage a wire rope.
o Lack of lubrication can significantly shorten the useful service life of a wire rope.
o Contact with electrical wire and the resulting arcing will damage a wire rope.
Find more information about Wire rope :
https://www.huahanmachinery.com/product/steel-wire-rope.html